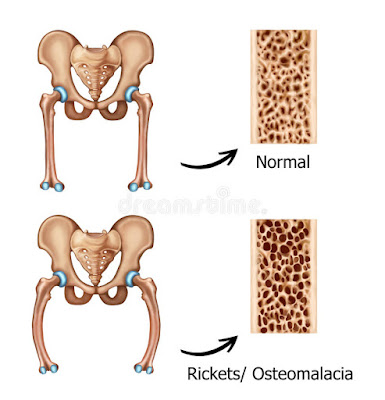
Rickets is a failure in the mineralization of growing bone. It is most commonly secondary to nutritional causes. In fully developed bone this is called Osteomalacia. The daily vitamin D requirements are 400 IU.
CAUSES
Vitamin D intake inadequate:
- Nutritional: Prematurity (osteopenia of prematurity), Breast-fed infants more at risk, Poorly fed infants (malnutrition).
- Malabsorption- coeliac disease, steatorrhoea, cystic fibrosis, Inadequate sunlight exposure (especially in dark-skinned).
Metabolism of vitamin D:
- Renal disease.NB: PO4 Increases
- Liver disease
- Anticonvulsants, e.g.phenytoin (metabolizes vitamin D)
Phosphate excretion increased:
- Familial hypophosphatemic rickets
- Vitamin D-dependent rickets - type I or type II (receptor defect)
- Fanconi syndrome
CLINICAL FEATURES
- Head - large anterior fontanelle with delayed closure (>2 years), craniotabes (ping-pong ball skull), frontal bossing.
 |
| Ping-pong ball skull |
- Chest - enlargement of costochondral junctions (Rachitic or rib rosary), Harrison sulcus, pigeon chest.
- Thickened wrists and ankles.
- Bowlegs, knock knees.
- Dwarfism, pot belly, muscular weakness, kyphosis, small pelvis, coxa vara.
- Late dentition with enamel defects.
- Greenstick fractures.
INVESTIGATIONS
- Biochemical investigations.
- X-ray of the left wrist (or left knee if <2 years):
- Widened epiphyseal plate
- Cupping and fraying of the metaphysis
- Increased joint space
- Line of calcifications seen when healing
- Cysts, subperiosteal erosions, fractures, Looser's zones, osteopenia if severe.
TREATMENT
This is with vitamin D in the necessary form:
- Nutritional rickets - Calciferol (D3)
- Renal disease - Alphacalcidol (1 alpha OHD3) or calcitriol (1,25(OH)2D3)


Comments
Post a Comment