Search This Blog
The blog aims to educate and knowledge sharing portal on pediatrics and the miscellaneous disease.
Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Screening for Down syndrome during pregnancy and at birth
Screening for Down syndrome is offered as a routine part of prenatal care in the United States. If you are a woman over 35, your baby's father is over 40, or there is a family history of Down syndrome, you may want to get an evaluation.
First trimester:
An ultrasound evaluation and blood tests can look for Down syndrome in your fetus. These tests have a higher false-positive rate than tests done at later pregnancy stages. If results are not normal, your doctor may follow up with an amniocentesis after your 15th week of pregnancy.
Second trimester:
An ultrasound and quadruple marker screen (QMS) test can help identify Down syndrome and other defects in the brain and spinal cord. This test is done between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy. If any of these tests are not normal, you will be considered at high risk for birth defects.
Additional prenatal tests:
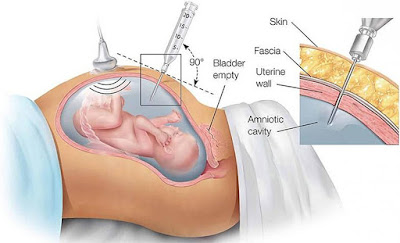
- Amniocentesis: Your doctor takes a sample of amniotic fluid to examine the number of chromosomes your baby has. The test is usually done after 15 weeks.
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS): Your doctor will take cells from your placenta to analyze fetal chromosomes. This test is done between the 9th and 14th weeks of pregnancy. It can increase your risk of a miscarriage, but according to the Mayo Clinic, only by less than 1 percent.
- Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS, or cordocentesis): Your doctor will take blood from the umbilical cord and examine it for chromosomal defects. It is done after the 18th week of pregnancy. It has a higher risk of miscarriage, so it is performed only if all other tests are uncertain.
Tests at birth
At birth, your doctor will:
- perform a physical examination of your baby
- order a blood test called a karyotype to confirm Down syndrome
Popular Posts
Diagnosis and treatment of Umbilical Hernia
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Overview and symptoms of Turner syndrome
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps



Comments
Post a Comment