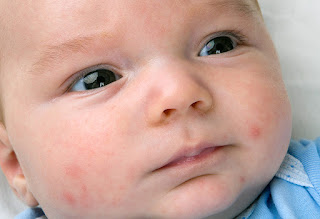
Acne is a common inflammatory disorder of the pilosebaceous unit, most common in teenagers and young adults. It is primarily due to increased sebum production from high androgen levels (oily skin, greasy hair). Androgen levels are high directly after birth which can cause infantile acne (due to maternal androgen which rapidly falls), an increase from age 9 years to teenage years. Lipophilic bacteria (especially propionibacterium acnes) colonize the hair follicles. The face, upper back, and chest are most commonly affected.
Lesions of acne
- Comedones (plugs of sebaceous material within hair follicle unit) (open comedones=blackheads: closed comedones= whiteheads)
- Papules, pustules
- Nodules, cysts
- Scars
Treatment
Topical- Antibacterial and keratolytic, e.g. benzoyl peroxide.
Antibiotic, e.g.erythromycin
Retinoic acid (can irritate the skin)
Oral - Antibiotics, e.g. erythromycin. Given for 6-12 months
Anti-androgens (girls only)- certain oral contraceptive pill formulations
Retinoid - isotretinoin, given at 1mg/kg dose usually over 4-6 months.
This decreases the size of the sebaceous glands and reduces sebum production and follicular hyperkeratosis. It is very effective, however, side effects include dry skin and lips, muscular aches, and teratogenicity. Elevated serum lipids and hepatitis (idiosyncratic) may occur ( monitor serum lipids and LETs).

Comments
Post a Comment