Search This Blog
The blog aims to educate and knowledge sharing portal on pediatrics and the miscellaneous disease.
Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Head and brain injuries during birth
Head injury is the most common birth-related injury.
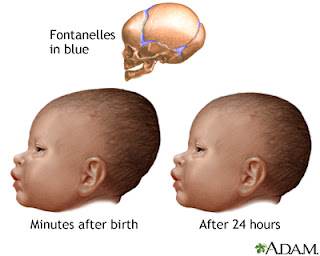
Head molding is not an injury. Molding refers to the normal change in the shape of the baby's head that results from pressure on the head during delivery. In most births, the head is the first part to enter the birth canal. Because a fetus's skull bones are not rigidity fixed in position, the head elongates as it is pushed through the birth canal, which allows the fetus to pass through more easily. Molding does not affect the brain and does not cause problems or require treatment. The head shape gradually becomes more rounded over several days.
Swelling and bruising of the scalp is common but not serious and generally resolves within a few days.
Scalp scratches can occur when instruments (such as monitor leads attached to the scalp, forceps, or vacuum extractors) are used during vaginal delivery.
Bleeding outside of the skull bones can lead to an accumulation of blood either above or below the thick fibrous covering (periosteum) of one of the skull bones.
A cephalhematoma is blood accumulation below the periosteum. Cephalohematomas feel soft and can increases in size after birth. Cephalohematomas disappear on their own over weeks to months and almost never require any treatment. However, they should be evaluated by the pediatrician if they become red or start to drain liquid.
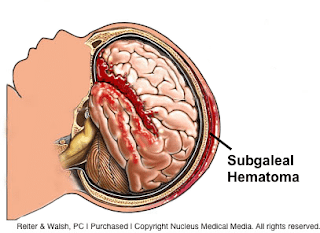
A subgaleal hemorrhage is bleeding directly under the scalp above the periosteum covering the skull bones. Blood in this area can spread and is not confined to one area like a cephalohematoma. It can cause significant blood loss and shock, which may even require a blood transfusion. A subgaleal hemorrhage may result from the use of forceps or a vacuum extractor or may result from a blood clotting problem.
Fracture of one of the bones of the skull may occur before or during the birth process. Unless the skull fracture forms an indentation (depressed fracture), it generally heals rapidly without treatment.
Popular Posts
Diagnosis and treatment of Umbilical Hernia
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Overview and symptoms of Turner syndrome
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps






Comments
Post a Comment