Search This Blog
The blog aims to educate and knowledge sharing portal on pediatrics and the miscellaneous disease.
Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Nerve injuries
Nerve injuries may occur before or during delivery. These injuries usually cause weakness of the muscles controlled by the affected nerve. Nerve injuries may involve the
- Facial nerve: Lopsided facial expression
- Brachial plexus: Arm and/or hand weakness
- Phrenic nerve: Difficulty breathing
- Spinal cord (rare): Paralysis
- The way the fetus was positioned in the uterus before birth
- The nerve being pressed against the mother's pelvis during delivery
- Forceps used to assist the delivery
A brachial plexus is a group of large nerves located between the neck and shoulder, leading to each arm. During a difficult delivery, one or both of the baby's arms can be stretched and injure the nerves of the brachial plexus and cause weakness or paralysis of part or all of the baby's arm and hand. The weakness of the shoulder and elbow is called Erb palsy, and weakness of the hand and wrist is called Kilumpke palsy. About half of the cases of brachial plexus injuries are related to difficult deliveries, typically involving large babies, and about half occur in babies with normal deliveries. Brachial plexus injury is less frequent in babies delivered by cesarean delivery. Extreme movements at the shoulder should be avoided to allow the nerves to heal. Many milder injuries resolve over a few days. If the abnormality is more severe or lasts for more than 1 or 2 weeks, physical therapy or occupational therapy for proper positioning and gentle movement of the arm are recommended. If there is no improvement over 1 or 2 months, doctors typically recommend the baby be evaluated by a pediatric neurologist and/or orthopedist at a pediatric specialty hospital to see whether surgery may be beneficial.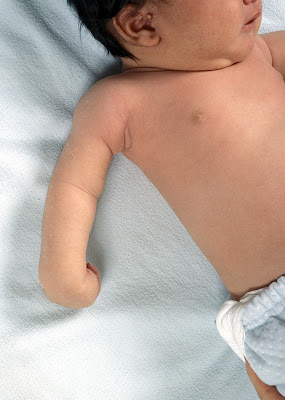
Erb palsy
The phrenic nerve, which is the nerve going to the diaphragm (the muscular wall that separates the organs of the chest from those of the abdomen and assists in breathing), is occasionally damaged, resulting in paralysis of the diaphragm on the same side. In this case, the newborn may have difficulty breathing and sometimes requires assistance with breathing. Injury of the phrenic nerve usually resolves completely within a few weeks.
Spinal cord injuries due to overstretching during delivery are extremely rare. These injuries can result in paralysis below the site of the injury. Damage to the spinal cord is often permanent. Some spinal cord injuries that occur high up in the neck are fetal because they prevent the newborn from breathing properly.
Other nerves, such as the radial nerve in the arm, the sciatic nerve in the lower back, or the obturator nerve in the leg, also may be injured during delivery.
Popular Posts
Diagnosis and treatment of Umbilical Hernia
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Overview and symptoms of Turner syndrome
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment