Search This Blog
The blog aims to educate and knowledge sharing portal on pediatrics and the miscellaneous disease.
Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Causes and Symptoms of DiGeorge syndrome
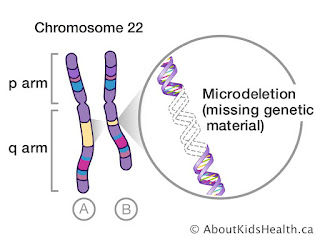
DiGeorge syndrome is caused either by the inheritance of a defective chromosome 22 or by a new defect in chromosome 22 in the fetus. The type of defect that is involved is called a deletion. A selection occurs when the genetic material in the chromosome does not recombine properly during the formation of sperm or egg cells. The deletion means that several genes from chromosome 22 are missing in children with DiGeorge syndrome inherited the deletion from a parent, while 94 percent had a new deletion.
The loss of the genes in the deleted material means that the baby's third and fourth pharyngeal pouches fail to develop normally during the twelfth week of pregnancy. This developmental failure results in a completely or partially absent thymus gland and parathyroid glands. In addition, 74 percent of fetuses with DiGeorge syndrome have severe heart defects. The child is born with a defective immune system and an abnormally low level of calcium in the blood.
These defects usually become apparent within 48 hours of birth. The infant's heart defects may lead to heart failure, or there may be seizures and other evidence of a low level of calcium in the blood (hypocalcemia).
Popular Posts
Diagnosis and treatment of Umbilical Hernia
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Overview and symptoms of Turner syndrome
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment